| Home > Products > Test kit for Potential Anti Oxidant (PAO) |
Rev.080604 |

|
|
Suitable for detection of total antioxidant capacity in serum and food extracts. For research use only. |
| Antioxidant assay: |
|
Oxidative stress plays on important role in various diseases and aging. The control of oxidative stress is expected to be useful to prevent
diseases and aging.Oxidative stress is caused by the imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidant defense system.
For accurate assessment of oxidative stress, measurement of ROS, oxidative damage and antioxidant activity may be essential. Recently,
antioxidants as functional foods which scavenge ROS attract a great deal of attention.
|
|
| Principle of this assay: |
|
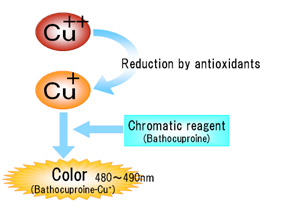
In the PAO assay kit, an easy and convenient method to measure antioxidant capacity is provided. Utilizing the reduction of cupric ion
(Cu++ to Cu+), antioxidant capacity of samples can be detected in 5 minutes. Samples are mixed with Cu++ Solution.
Cu++ are reduced by antioxidants to form Cu+. Reduced Cu+ react with Chromatic Solution (Bathocuproine) ,
and can be detected by absorbance at wavelength 480 to 490 nm. Antioxidant capacity can be calculated from the Cu+ formed.
PAO can detect not only hydrophilic antioxidants such as Vitamin C, glutathione, but also can detect hydrophobic antioxidants such as Vitamin E.
Applicable for assessment of total antioxidants of serum, foods and beverage samples.
|
|
 |
| Specifications: |
| Method: |
Colormetric assay(detection: 480 - 492 nm) |
| Assay range: |
21.9 - 4378 µmol/L (cupric ion reducing power) |
| Format: |
96 wells |
| Storage: |
Room temperature (10 - 25°C) |
| Applications: |
Human and animal serum samples, foods and beverage samples. |
| Required but not provided: |
A micro plate reader (measuring wavelength 492 nm)
Pipettes and pipette chips
Plastic test tubes
Distilled water
NaOH, HCl solution and pH meter (Not required if standards are prepared with distilled water only).
|
|
 |
| Content of this kit: |
| Standard (Uric acid powder): |
1 vial |
| Sample diluent: |
1 bottle |
| Cu++ solution: |
1 bottle |
| Stop solution: |
1 bottle |
| Micro titer plate: |
1 plate (96 wells) |
|
 |
| Assay procedure: |
| 1) |
Prepare 6 levels of standards by diluting 2mM uric acid. |
| 2) |
Please prepare plastic test tubes for 6 levels of standards and each sample.
Pour 390 µL of Sample Diluent, and add 10 µL of standards or diluted samples. |
| 3) |
Pour 200 µL of mixture to Micro titer plate. Use 200 µL of
Sample Diluent for blank well. |
| 4) |
Read absorbance at 490 nm (as READ1). |
| 5) |
Add 50 µL of Cu++solution to each well, mix gently,
and incubate at room temperature for 3 minutes. |
| 6) |
Add 50 µL of Stop solution, mix gently, and read absorbance
at 490 nm (as READ2). |
| 7) |
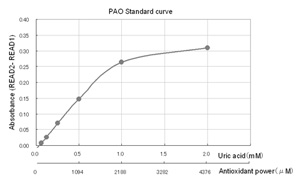
Please draw standard curves by plotting the difference of absorbance
readings (READ2 - READ1) as vertical axis, and concentration of uric acid standards (mM) as horizontal axis.
Calculate the corresponding uric acid concentration of samples. Multiply corresponding uric acid concentration (mM)
of samples by 2189, to estimate antioxidant power (µmol/L).
1mM of uric acid = 2189 µmol/L (copper reducing power) |
|
 |
| References |
| 1) |
Oxidative imbalance and cathepsin D changes as peripheral blood biomarkers of Alzheimer disease:
A pilot study
E Strafacea, P Matarresea, L Gambardella, R Vona, A Sgadari,MC Silveri, W Malorni
FEBS Letters 579, p2759-766 (2005) |
| 2) |
Oxidative stress and its association with coronary artery disease and different atherogenic risk factors
C. VASSALLE, L. PETROZZI , N. BOTTO, M. G. ANDREASSI and G. C. ZUCCHELLI
Journal of Internal Medicine 256, p308-315(2004) |
| 3) |
Antioxidant capacity as a reliable marker of stress in dairy calves transported by road
P Pregel, E Bollo, FT Cannizzo, B Biolatti, E Contato, and PG Biolatti
Veterinary Record 156, p53-54 (2005) |
| 4) |
Vitamin E-coated dialyzers reduce oxidative stress related proteins and markers in hemodialysis ?
a molecular biological approach.
LA Calo, A Naso, E Pagnin, PA Davis, M Castoro, R Corradin, P Riegler, C Cascone, W Huber and A Piccoli
Clinical Nephrology, Vol.62(5), p355-361 (2004) |
| 5) |
Oxidative stress-related factors in Bartter's and Gitelman9s syndrome: relevance for
angiotensin IIsignalling.
Calo LA, Pagnin E, Davis PA, Sartori M, Semplicini A.
Nephrol Dial Transplant 18(8) p1518-1525 (2003) |
| 6) |
Effect of epoetin on HO-1 mRNA level and plasma antioxidants in hemodialysis patients.
Calo LA, Stanic L, Davis PA, Pagnin E, Munaretto G, Fusaro M, Landini S, Semplicini A, Piccoli A.
Int. J Clin. Ther 41(5), p187-192 (2003) |
| 7) |
Restored Antioxidant Capacity Parallels the Immunologic and Virologic Improvement in Children with
Perinatal Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection Receiving Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy.
M Martino, F Chiarelli, M Moriondo, M Torello, C Azzari, and L Galli
Clinical Immunology 100(1),p82-86 (2001) |
|
 |
| |
| Product name |
Code |
Assay range |
Assay time |
Format |
| Test kit for Potential Anti Oxidant (PAO kit) |
KPA-050 |
21.9-4378 µmol/L |
5 min. |
96 wells |
|
Related patent: US PAT.6613577, JP PAT.5917951.
Made in Japan. |
How to order
|
|
|
| Contact technical support |
|
|
[NOTICE]: Our products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Not for diagnostic, medical or other use.
We are making efforts to prevent errors or mistakes on preparing web site documents, instruction manuals and products.
But even if some damage would causedby such faults, we will be exempt from responsibility.
|
Copyright ©
Genox Corporation. All rights reserved.
|


 )
)